What Is HVAC? A Comprehensive Guide
Sharing your quote takes less than a minute

When it comes to home comfort systems, you may have heard the term HVAC thrown around before. But what is HVAC exactly? HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning and includes all of the heating and cooling equipment that you rely on to stay safe and comfortable throughout the year – whether it's cold and icy or hot and humid outside.
Often, it’s only when issues arise, or a sudden breakdown occurs that we truly recognize the significance of our heating and air conditioning systems and our limited knowledge about how they operate.
To gain a clearer understanding of “what is an HVAC system” and how it functions, HVAC.com compiled this informative guide to address the question: What is HVAC?
What Does HVAC Stand For?
HVAC encompasses all of the heating, cooling, ventilation, and indoor air quality equipment in your home. Let’s take a closer look at what each component of HVAC entails:
- Heating. A functioning heating system is crucial to keep you warm and safe during colder months. Even homes and businesses in the South and Southwest require some type of heating system as temperatures can dip near or below freezing during the winter. Common heating systems include gas furnaces, heat pumps, boilers, radiators, and space heaters.
- Ventilation. Ventilation is the process of bringing fresh air into an enclosed space and removing stale or polluted air to maintain a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. In HVAC, “mechanical ventilation” describes your HVAC system’s air handler, ducts, and return vent’s ability to control indoor temperatures and balance humidity levels. It also entails vents to exhaust harmful gases out of the home created during the heating process.
- Air Conditioning. Air conditioning keeps us cool and comfortable during the warmer months and is a necessity in most areas of the country due to rising temperatures associated with Global Warming. Common cooling systems include central air conditioners, window ACs, heat pumps, and ductless mini-split systems.
What Does HVAC Mean, and What Is the Purpose of HVAC Systems?
So what is an HVAC system exactly? Life in most regions of the country would be downright miserable without a properly functioning heating and air conditioning system. HVAC systems play a critical role in creating and maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment in homes and commercial and industrial settings. An HVAC system’s primary objective is to regulate temperature, humidity, air quality, and airflow to ensure optimal occupant comfort, health, and productivity.
In essence, the purpose of an HVAC system goes beyond merely controlling temperature; it encompasses creating a balanced indoor climate that aligns with human comfort and health requirements. These systems integrate heating, cooling, ventilation, and humidity control to create spaces that are pleasant, safe, and conducive to the activities and needs of the occupants, whether it’s a home, office, hospital, or industrial facility.

How Do HVAC Systems Work, and What Are the Different Type of Systems?
Are you still asking yourself – “how do HVAC systems work?” Let’s delve a little deeper into the different types of HVAC systems, their components, and how they operate.
Central Air Conditioners
Central air conditioning systems consist of an outdoor condenser unit (the big box next to your home) which houses the compressor, and an indoor air handler which uses a blower to push air into the ductwork and throughout your living areas. Central air conditioners are the most common type of cooling system.
To provide cooling, the system’s refrigerant, located inside the evaporator coil, extracts heat and excess humidity from the indoor air to effectively cool a home. To balance humidity levels, the moisture is funneled out of your home through an AC condensate drain line.
Portable, window, and ductless mini-split cooling systems are popular alternatives to cool smaller spaces.
Heat Pumps
In existence for decades, heat pumps have gained traction in recent years as an eco-friendly and efficient alternative to heating systems that burn fossil fuels such as oil and gas to generate heat.
Air-source heat pumps are unique in that they provide both heating and cooling for year-round comfort. Modern heat pumps with advanced technology can operate efficiently in temperatures as low as zero degrees Fahrenheit. However, some heat pumps require a supplemental heating source, such as electric heat strips or a gas furnace, when temperatures drop too low.
During the warmer months, air-source heat pumps work similarly to central air conditioners by using a refrigerant to extract heat from indoors and expelling it outside through the compressor. While operating during the cold-weather months, heat pumps utilize a reversing valve to switch from cooling to heating modes to operate in reverse. Heat pumps use refrigerant to extract heat from outdoors to warm living areas. If you're considering buying a heat pump, check with your local HVAC dealer about available HVAC energy tax credits.
Geothermal heat pumps, meanwhile, share similarities with air-source heat pumps, but they operate differently. Instead of exchanging air between a home and the outside, geothermal systems utilize the Earth’s consistent temperature to exchange heat with a fluid. This fluid is compressed and expanded to either provide indoor heating by transferring warmth or outdoor cooling by dissipating heat.
Ductless Mini-Splits
Ductless mini-splits, also referred to as ductless heat pumps and ductless air conditioners, can provide both heating and cooling like traditional heat pumps. However, as their name suggests, they don’t require ductwork to distribute conditioned air. Instead, they consist of an outdoor condenser unit, one or more indoor air handling units installed on ceilings or walls, and a conduit that contains the refrigerant tubing, suction tubing, and condensate drain line that connects the outdoor unit with the indoor unit.
Although ductless-mini splits can be installed in rooms throughout homes to create temperature zones, they are typically used to heat and cool just one room or area. Some of the popular applications for a ductless system include:

- Bonus rooms over garages and sunrooms that are difficult to keep comfortable.
- Converting garages, basements, and attics, which are not connected to the central HVAC system, into workable or livable spaces.
- New home additions.
- Guest houses.
A lack of ductwork makes ductless systems highly efficient, as it’s estimated 20% or more of conditioned air is typically lost through leaky ducts or poorly insulated ductwork.
Furnaces
Gas furnaces are a popular choice to heat homes during the colder months, especially in northern portions of the country. Gas furnaces provide powerful, consistent heat to quickly reach the temperature on your thermostat for optimal savings and comfort.
A forced-air furnace heats air inside the system and uses a heat exchanger to transfer the heat from the combustion process to the indoor air without allowing combustion gases to leak out. Fuel sources for forced air furnaces consist of natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity.
Boilers
Utilizing the concept of thermal exchange, boilers provide heating for homes and businesses using fuel sources such as natural gas, oil, or electricity, generating either steam or hot water confined within a sealed chamber. The energy derived from fuel combustion is conveyed to the water or steam, elevating their temperature and pressure, with hot water systems distributing warmth through pipes to radiators or underfloor heating, thereby emanating heat throughout the environment.
Commercial HVAC Systems
An efficiently operating commercial HVAC system is essential for maintaining a thriving business. Unexpected malfunctions can lead to lost business and diminished employee productivity. Some common commercial HVAC systems include:
- Rooftop units (RTUs) are popular for their space-saving installation on building rooftops, providing both heating and cooling functions.
- Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems offer precise control over individual zones by adjusting refrigerant flow to match varying demand.
- Chilled Water Systems circulate cold water through coils for cooling and are ideal for larger buildings with substantial cooling requirements.
- For increased energy efficiency, Dedicated Outdoor Air Systems (DOAS) focus on ventilation by conditioning outdoor air separately and then distributing it indoors.
- Finally, Split Systems divide components between indoor and outdoor units, connecting them via refrigerant lines, offering versatile solutions for various commercial settings.
The Components of a Typical HVAC System
To better understand “what is HVAC,” it's important to know what makes up a heating and cooling system. A typical HVAC system consists of several key components working together to maintain indoor comfort and air quality.
- The main unit: Conventional HVAC setups encompass core systems including central air conditioners, heat pumps, furnaces, or boilers. While the traditional arrangement often pairs a gas furnace with a central air conditioner, the trend toward integrating heat pumps is expanding, given their capability to offer comprehensive heating and cooling solutions throughout all seasons.
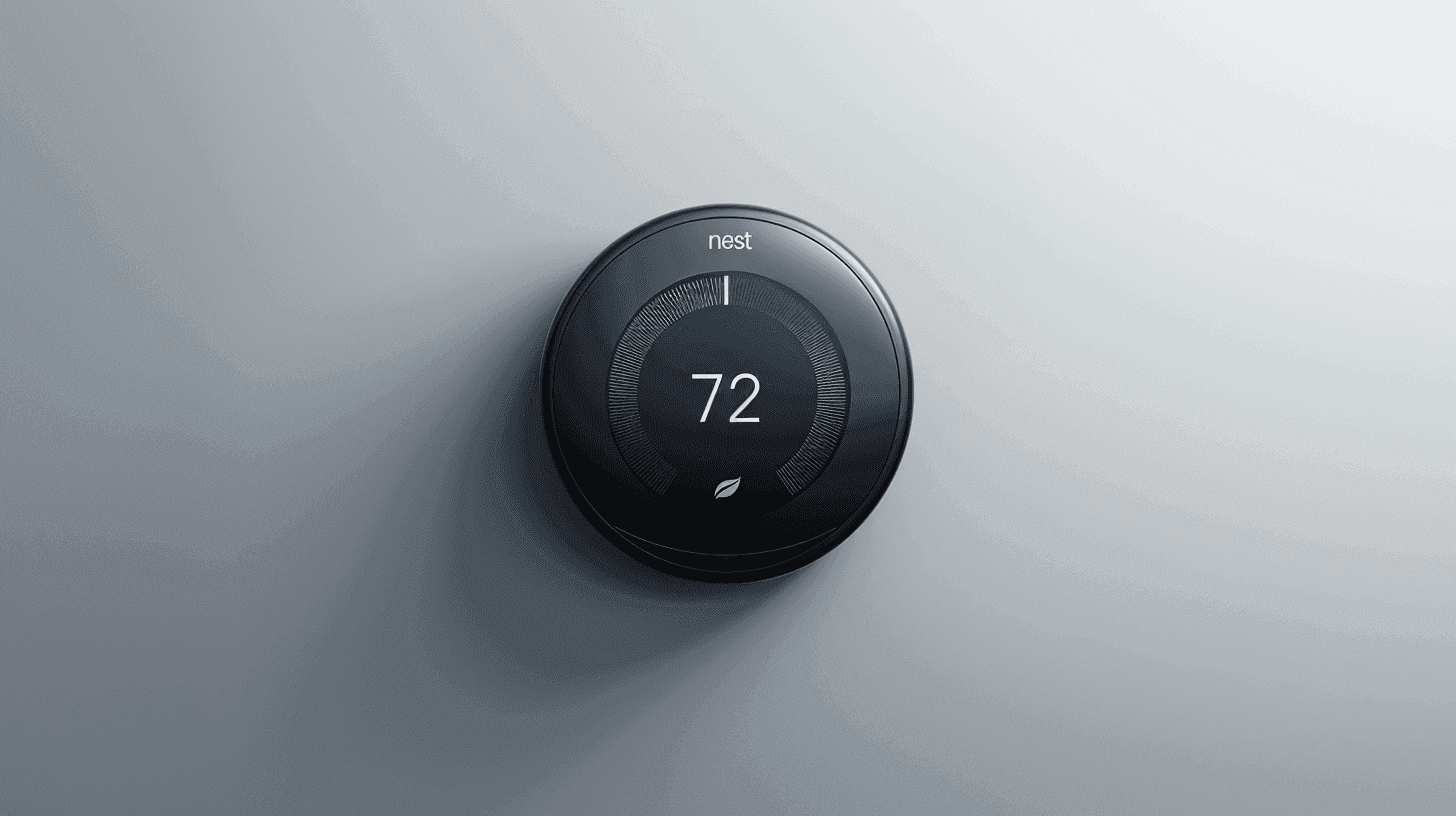
- Thermostat: Called the “brain” of an HVAC system, the thermostat tells the system when to turn on and off based on its temperature settings. The most common types of thermostats include manual, programmable, and smart thermostats. The latter offers the most convenience and efficiency, allowing you to control the temperature remotely from your smartphone or smart device.
- Evaporator Coil: Located inside the indoor unit, the evaporator coil absorbs heat from the indoor air, allowing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the air.
- Condenser Coil: Situated in the outdoor unit, this coil releases heat absorbed from indoors into the outdoor air as the refrigerant condenses.
- Refrigerant: Used in air conditioning systems and heat pumps, the refrigerant transfers heat outdoors to cool a building. Heat pumps also use refrigerant to provide warmth in the winter by extracting heat from the outside and transferring it indoors.
- Heat exchanger. A furnace’s heat exchanger is a device designed to efficiently transfer thermal energy between two or more fluid mediums, such as gases or liquids, without them coming into direct contact.
- Air Handler: The indoor air handling unit contains the evaporator coil, blower, air filter, and sometimes additional components. It circulates conditioned air throughout the building via a network of ducts.
- Blower Fan: The blower fan pushes air through the HVAC system’s ductwork and into indoor spaces.
- Ductwork: The ducts consist of a network of passages that distribute conditioned air throughout the building and return air to the system.
- Vents/Registers: Vents and registers are opening in walls, floors, or ceilings where conditioned air enters rooms and where return air is collected.
- Air Filters: HVAC air filters remove dust, debris, and particles from the incoming air before it’s conditioned and distributed.
Top HVAC Manufacturers in 2023
The top HVAC manufacturers in the industry offer a range of choices for consumers seeking heating, ventilation, and air conditioning solutions. Some of the most respected and reputable brands in no particular order include:

HVAC Maintenance
Residential and commercial HVAC systems require regular maintenance to perform efficiently and reliably, preventing unexpected breakdowns and increasing the system’s lifespan.
HVAC tune-ups should ideally be performed twice a year; once before the heating season and again before the cooling season. The area you live in and the type of system you own dictate the timing of HVAC maintenance.
During an HVAC tune-up, a qualified HVAC technician inspects the entire system for any issues, calibrates and cleans necessary components and recommends any needed repairs before they turn into bigger and more expensive issues.
Many reputable HVAC companies offer maintenance plans that provide yearly tune-ups at a discounted price, as well as other benefits including priority service and discounts on repairs.
DIY HVAC Maintenance Tips
In between maintenance visits, homeowners should replace their HVAC air filters every 2-3 months or according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Clogged and dirty air filters reduce the system’s airflow, which leads to insufficient performance, high energy bills, an increased chance of repairs, and complete system breakdowns.
It’s also recommended to clear debris such as twigs and leaves away from the outside AC unit or heat pump to prevent inefficient airflow and regularly trim vegetation around the unit to maintain a clear space of 1-2 feet on each side. This allows for proper airflow and efficient heat exchange.
HVAC Repair
Like all mechanical equipment, HVAC systems eventually develop issues that require repair, especially aging and inefficient systems. In some cases, HVAC replacement is a better solution than HVAC repair.
If your unit is under 10 years old, a repair often makes the most sense. In most cases, a simple repair will return your HVAC system to proper working condition. Contact a reputable HVAC company if you notice any of the following issues with your system:
- Inadequate heating or cooling
- Strange noises
- Unpleasant odors
- Weak or no airflow
- A clogged condensate drain line
- Uneven heating or cooling
- Short cycling
- High energy bills
- Refrigerant leaks
Sharing your quote takes less than a minute